Visual Diagnosis Week 4
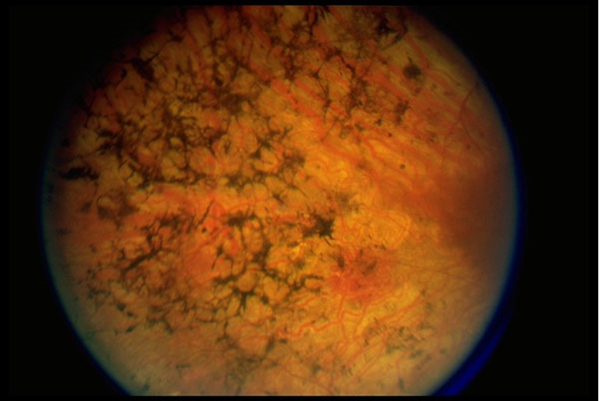
1. This is the fundoscopic exam of a 20 year old who has experienced progressive peripheral vision loss during his teen years. He now is beginning to have nyctalopia. Based on his ocular symptoms and exam, you give him a diagnosis of _________. Name three other syndromes with which this ophthalmologic diagnosis is associated.
Diagnosis: Retinitis Pigmentosa
Other syndromes with which it is affliated: Usher Syndrome, Kearns-Sayre syndrome, abetalipoproteinemia, neurosyphilis, toxoplasmosis, Refsum’s disease, Waardenburg syndrome, Alport syndrome, mucopolysaccharidoses (eg, Hurler syndrome, Scheie syndrome, Sanfilippo syndrome) , Bardet-Biedl syndrome, Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis
What is it?: Inherited form of progressive peripheral vision loss and night vision problems. Many gene defect pathways can lead to this same outcome. The most common systemic association is hearing loss. The genetic defect that occurs leads to destruction of the rod photoreceptors, leading to a rod-cone dystrophy. The average age of first presentation is in early adulthood, but it can begin in infancy. The classic exam finding is the above-pictured “bone spicule” pattern on fundoscopic exam (= midperipheral retinal hyperpigmentation)
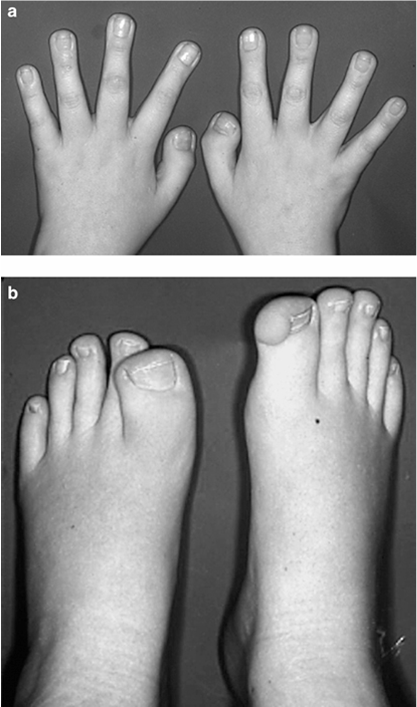
2. Name this syndrome and 3 of its other clinical manifestations.
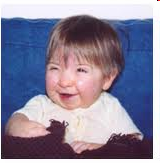
Dx: Rubenstein-Taybi Syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Other Clinical Manifestations:
Prominent beaked nose
Antimongoloid palpebral fissures Low-set/malformed ears
Strabismus
Microcephaly
Crowded irregular teeth, high palate, short upper lip, and protuberant lower lip
Broad great toes
Broad thumbs with radial angulation
Broad fingers
Syndactyly, polydactyly, and ulnar deviation of the thumb
Strabismus
Congenital or juvenile glaucoma
Retinal abnormalities
Mental retardation
Speech difficulties
Hypotonia
Growth retardation
Retarded osseous maturation
Vertebral and sternal abnormalities
Patellofemoral instability
Fourth cuneiform bones
Hirsutism
Capillary nevus of the forehead or the nape
Cardiac anomalies
ECG abnormalities
Cryptorchidism
Gastroesophageal reflux
Constipation
Laryngeal wall collapsibility
Mood disorders and obsessive compulsive disorder